“Publicly traded companies” are businesses that have their shares listed on a stock exchange, making them available for the general public to invest in these shares. “Shares” represent a small portion of ownership in publicly traded companies. This also means that any stock market investor can become a shareholder and own a part of a company by buying shares from the Stock Market.
Understanding Publicly Traded Companies
Let us understand what a publicly traded company is, with the help of a fictional example of ‘Company X‘ in the IT sector. Company X has been consistently making profits, and now its management decides that they need to expand by adopting the latest technology. However, such expansion requires a huge amount of capital. Therefore, the management decides to raise funds from the public.
After approval from the regulatory authorities, they come up with an Initial Public Offering (IPO), after which Company X is listed on the stock exchange. Company X is now a publicly traded company, and any investor can buy and sell shares of Company X.
As a publicly traded company, Company X must comply with various regulations to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability. This includes regularly disclosing financial information, adhering to corporate governance standards, and ensuring fair business practices.
Regulation of Publicly Traded Companies: Ensuring Transparency and Investor Protection
Publicly traded companies are regulated by specific entities that vary from country to country. For example, in the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is the primary regulator, enforcing laws such as the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. In India, the main regulatory body is the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which works closely with stock exchanges such as the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE). In the European Union (EU), on the other hand, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) oversees securities markets in member states. Individual countries within the EU may also have their own regulations.
Regulation of Publicly Traded Companies aims to achieve several goals:
Investor Protection
An investor can decide to invest in a publicly traded company only if he has accurate information about the company. This is possible only when the company accurately discloses its financial position, ownership structure, and potential risks. This is where regulatory authorities play a key role. They ensure that publicly traded companies disclose the necessary information to investors.
Company Accountability
Publicly traded companies have a responsibility to their shareholders and the broader Stock Market. Regulations ensure responsible governance and discourage fraudulent activity on the part of both the investors and the publicly traded companies.
Market Fairness
Regulation of publicly traded companies prevents insider trading, market manipulation, and other illegal practices that give some investors an unfair advantage.
Benefits of being a Publicly Traded Company
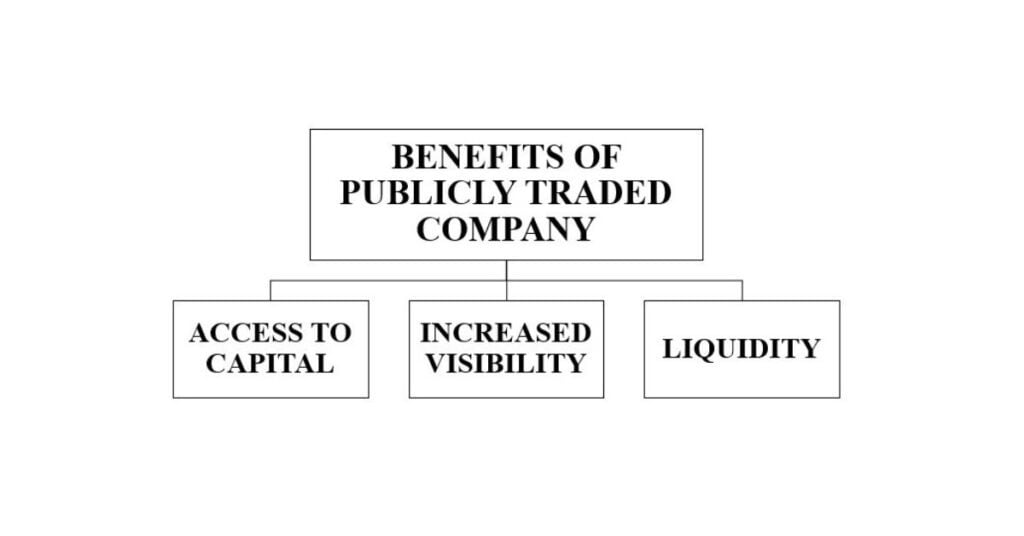
Access to capital
Publicly Traded Companies can raise a large amount of money by selling shares to the public. The funds raised from such selling activity can be utilized for expansion or adoption of latest technologies to accelerate the company’s business growth.
Increased visibility
Publicly Traded Companies have a higher public profile which plays a major role in attracting new customers and partners.
Liquidity
Shareholders can easily buy and sell shares of Publicly Traded Companies, making the shares more attractive to investors.
Drawbacks of being a Publicly Traded Company
Increased scrutiny
Publicly Traded Companies are subject to a high degree of scrutiny from investors, analysts, the media, and governments.
Short-term focus
Publicly Traded Companies may face pressure to focus on short-term profits rather than long-term growth in order to keep the investors interested in the stock.
Regulatory compliance
Publicly traded companies must comply with a complex set of regulations, which can sometimes make it difficult for them to focus on long-term development and research.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a company that is publicly traded?
A Publicly Traded Company is one that has its shares listed on the stock exchange. Investors can buy and sell these shares, which is profitable not only for the shareholders but also for the company.
What is an example of a public company?
A well-known example of a public company is Apple Inc. It is listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the ticker symbol AAPL. As a publicly traded company, Apple’s shares are available for purchase by any investor in the US stock market.
How do you know if a company is publicly traded?
You can determine if a company is publicly traded by checking major stock exchanges such as the NYSE, NASDAQ, NSE, BSE, or others. Alternatively, financial platforms and regulatory filings provide accessible information on publicly listed companies, while official company websites often provide stock listing details and financial reports.